Velvet fabric / Terciopelo is a beloved textile with a storied history, recognizable for its characteristic soft, luxurious texture and versatility. This article explores its origins, production process, types, applications, and environmental impact, along with its enduring popularity in both fashion and interior design.
What is Velvet Fabric / Terciopelo?
Velvet is a plush fabric featuring a smooth, dense pile that exudes elegance and opulence. The fabric’s soft texture and light-reflecting properties make it a practical and stylish choice for clothing and furnishings alike.
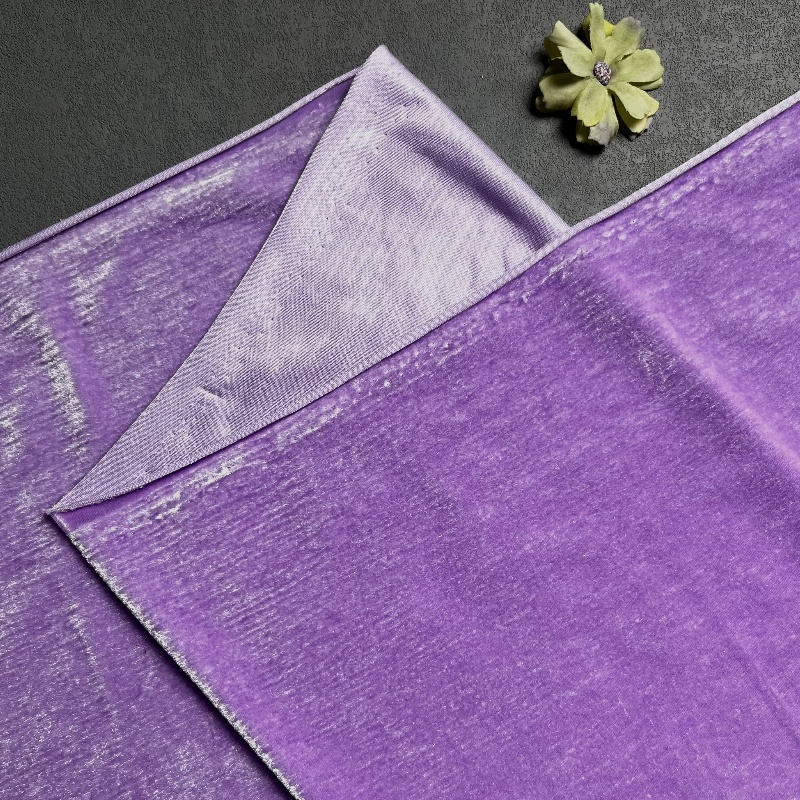

Construction and Composition
Velvet is created using a face-to-face method of weaving, where two layers of fabric are produced simultaneously and connected by warp yarns woven over rods or wires. During the process, a knife cuts through the middle, separating the layers and forming the fabric’s signature pile. These two lengths of fabric are then wound onto separate rolls.
This complex process was historically labor-intensive, making velvet a luxury item before the advent of industrial power looms. Even today, high-quality velvet remains a relatively costly fabric. Velvet is also challenging to clean due to its pile structure, though modern dry-cleaning techniques make maintenance more feasible.
The pile of velvet is created by cutting warp yarns, while velveteen pile is formed by cutting weft yarns, resulting in distinct textures and finishes.
Velvet can be made from a variety of fibers, including:
- Silk: The most luxurious and expensive option, often blended with rayon or cotton to reduce costs.
- Cotton: Results in a softer, less shiny fabric.
- Linen, Mohair, and Wool: Used for unique textures and finishes.
- Synthetic Fibers: Commonly polyester, nylon, viscose, or acetate, often blended with natural fibers for durability and stretch (e.g., “stretch velvet / velvet licrado” includes spandex).
Additionally, “Kuba velvet,” made from raffia palm fibers by the Kuba people of the Democratic Republic of Congo, represents a traditional approach to velvet-making. Modern synthetic blends offer affordability and versatility, while silk velvet can cost several hundred U.S. dollars per yard.
Velvet’s pile can be cut in two ways:
- Pile Up: Creates more shine and vibrancy.
- Pile Down: Produces deeper, richer color saturation.
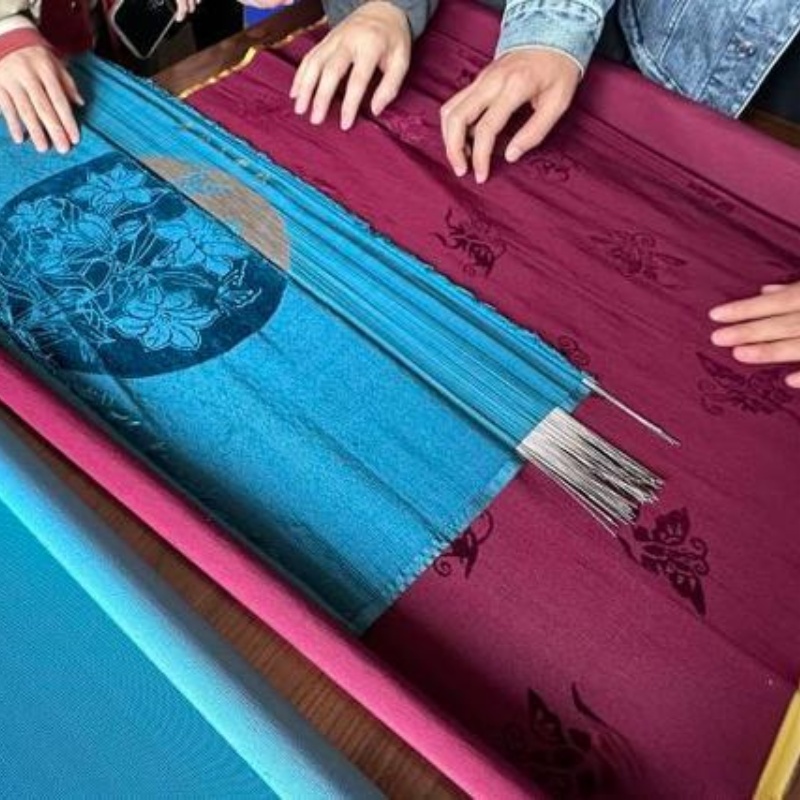

A Brief History of Velvet Fabric
Velvet’s origins date back to ancient Egypt and the Middle East, where luxurious textiles were highly prized. It later gained prominence during the Italian Renaissance as a symbol of wealth and status. Today, velvet remains synonymous with sophistication, adorning everything from formal wear to home furnishings.
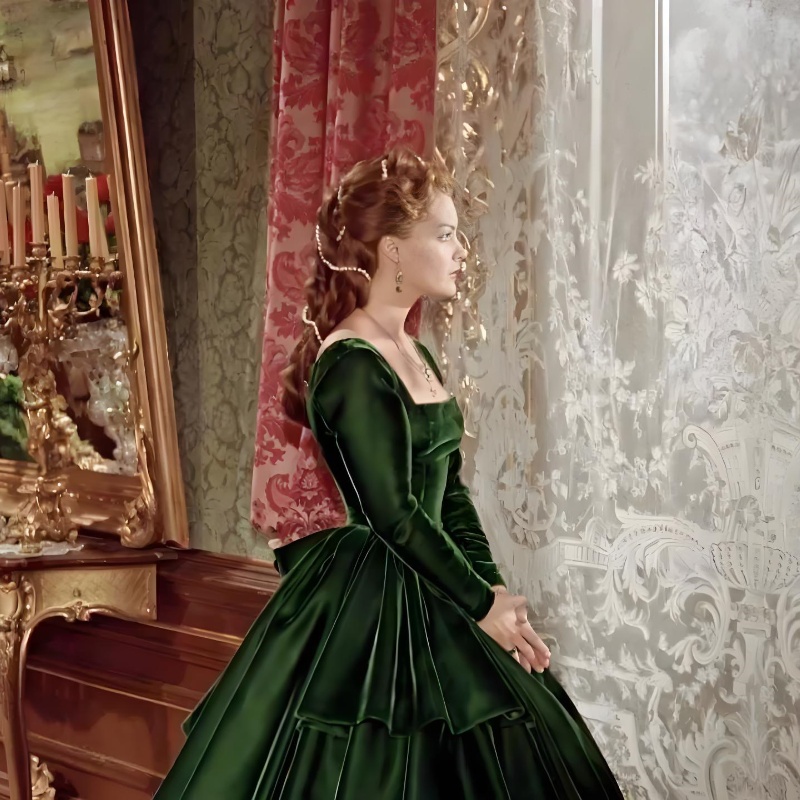

How is Velvet Fabric Made?
The production of velvet involves several meticulous steps:
- Weaving: A dual warp and pile weave is created using materials like silk, cotton, or synthetic fibers.
- Cutting and Brushing: The loops of the pile are carefully cut and brushed to create the fabric’s signature texture.
- Dyeing: Velvet is dyed in rich, vibrant hues that enhance its luxurious appearance.
Modern innovations include machine-weaving techniques that have made velvet more accessible while preserving its opulent appeal.
Types of Velvet
Velvet comes in a variety of forms, each with unique characteristics:
- Crushed Velvet: Features a textured, shimmering effect, often used in evening wear.
- Stretch Velvet: Infused with spandex for flexibility, suitable for form-fitting garments.
- Velveteen: A less plush variant, ideal for casual apparel.
- Embossed Velvet: Decorated with patterns pressed into the pile, perfect for upholstery and fashion.
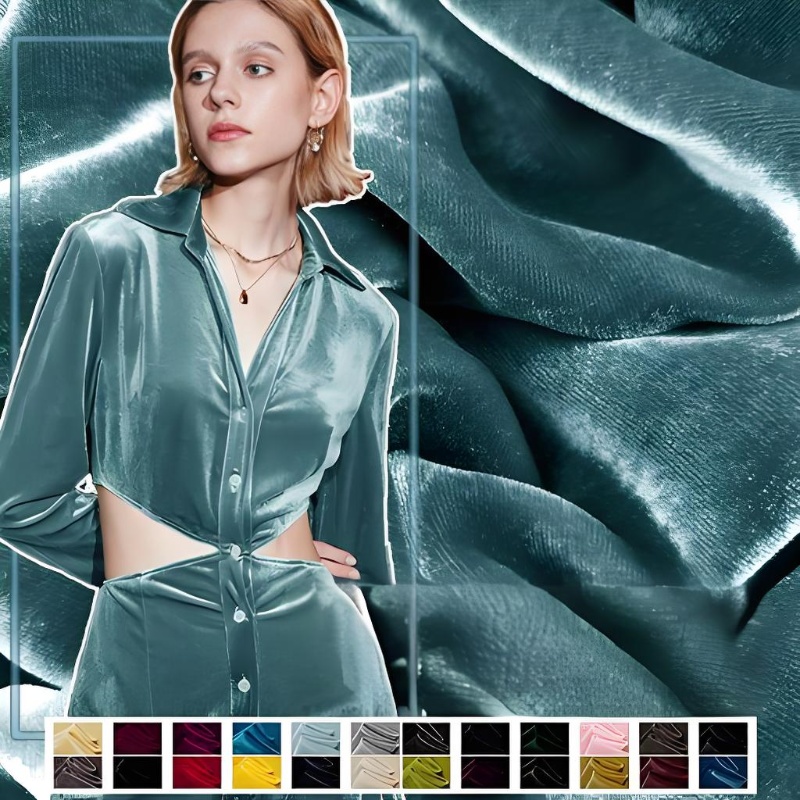


Applications of Velvet
Fashion and Apparel:
Velvet’s luxurious feel and appearance make it a favorite for evening gowns, blazers, and accessories. Its adaptability has also brought it into more casual, everyday wear.
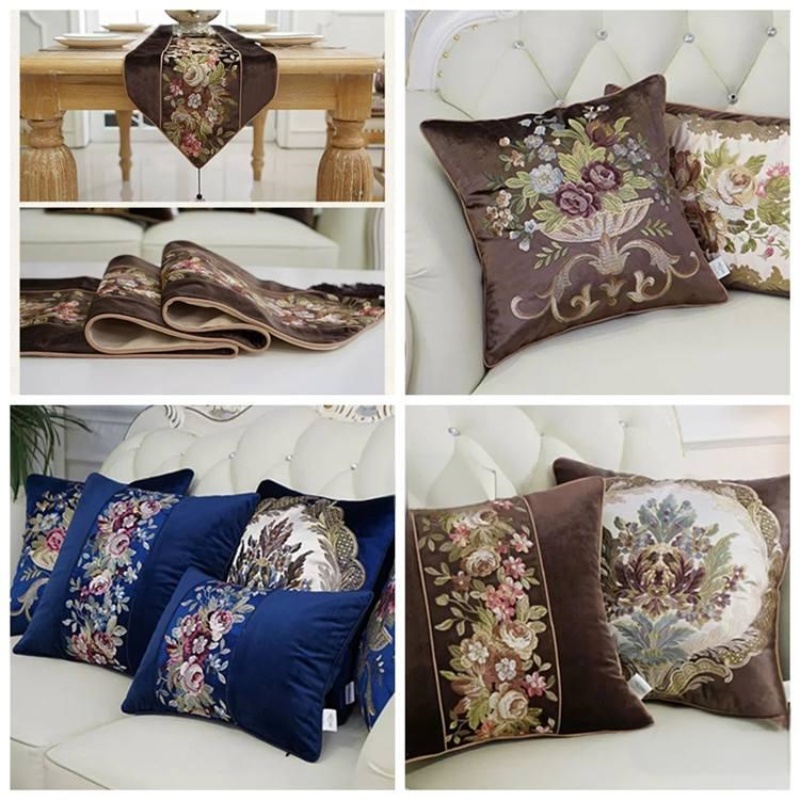
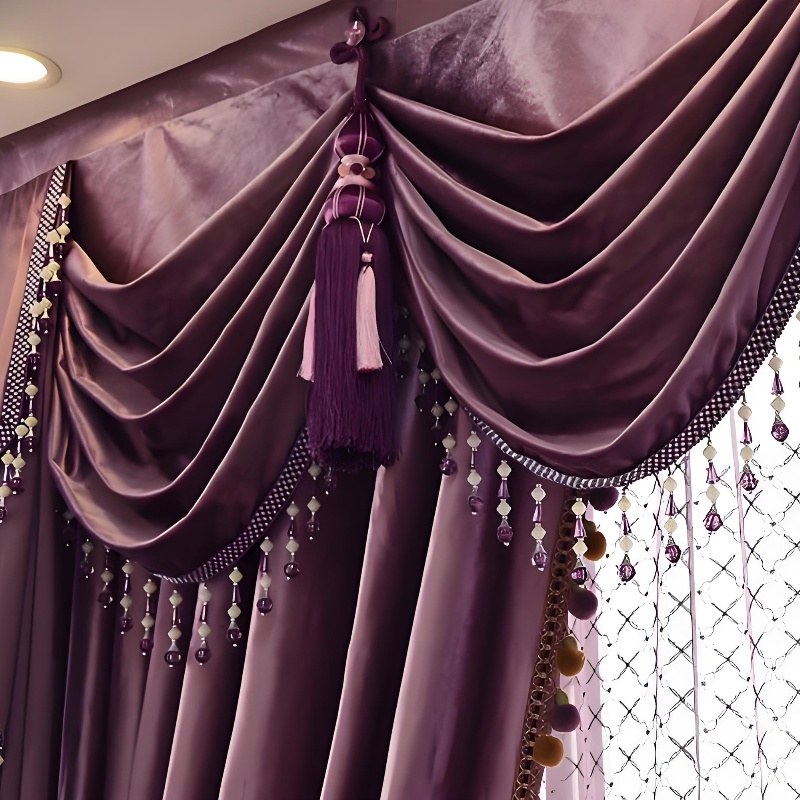
Home Furnishings:
In interior design, velvet is prized for its rich texture and comfort, often used for upholstery, curtains, and decorative cushions.


Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Velvet’s sustainability depends on its fiber composition:
- Natural Fibers (Silk and Cotton): Biodegradable but may involve resource-intensive production.
- Synthetic Fibers (Polyester): Durable and cost-effective but non-biodegradable.
The growing demand for eco-friendly velvet options, such as organic cotton and recycled polyester, is helping reduce its environmental impact.

Global Production
China and India are major producers of velvet, leveraging advancements in textile technology to streamline production and enhance quality. Italian velvet, however, remains a benchmark for luxury and craftsmanship.

Conclusion
Velvet is a fabric that embodies timeless elegance, durability, and style. From its royal origins to its modern applications, velvet continues to inspire designers and consumers alike. With innovations in sustainable production, this classic textile is set to maintain its allure for future generations.





